
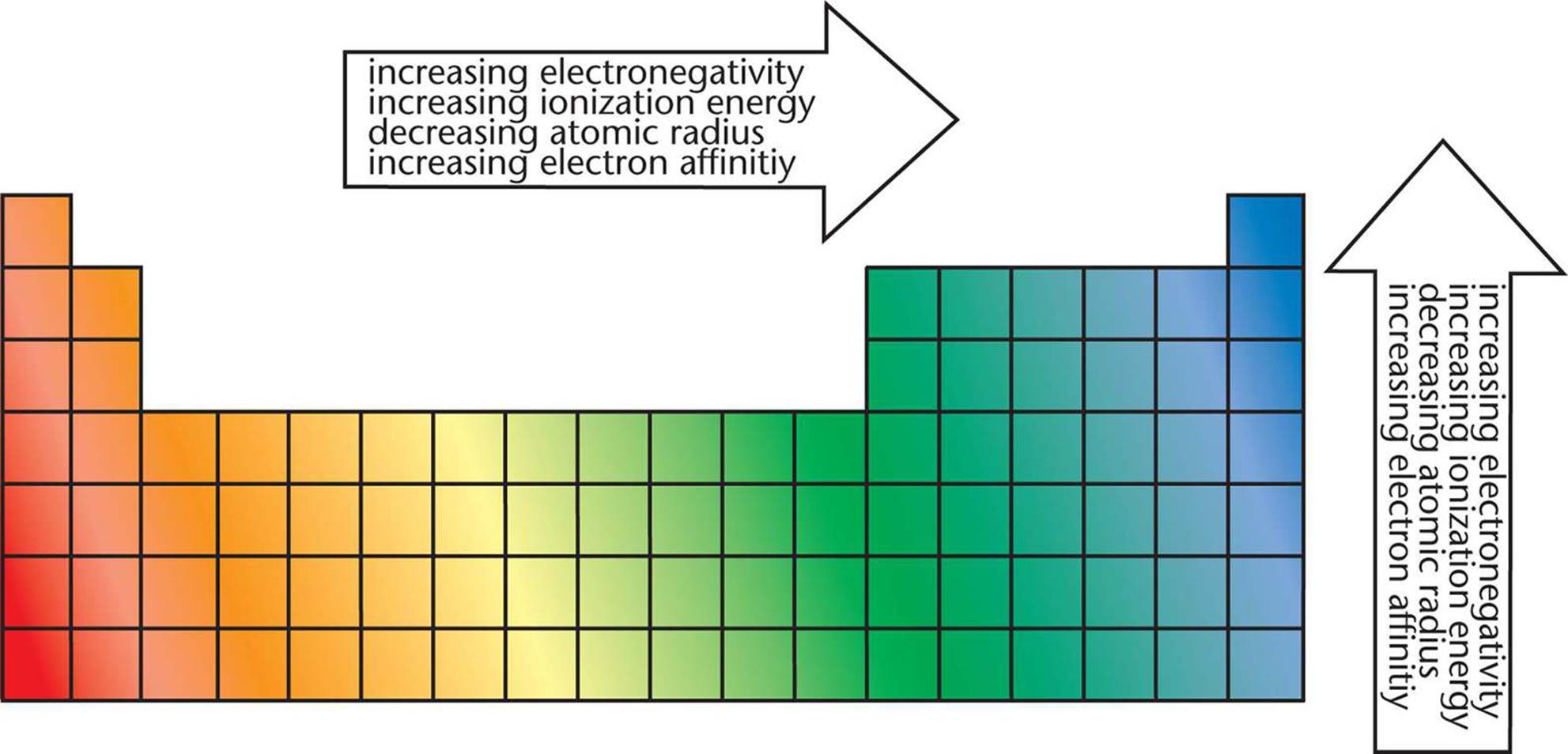
The Ionization energy increases further right down the period, and higher up a group as more energy is required to remove a tightly bounded electron from the atom. This property is describing the difficulty of removing an electron. The minimum amount of energy required to remove an electron from a neutral atom’s outermost electron shell in the gaseous phase is called the ionization energy. Note: This periodic trend excludes the Noble gases (Group 18). Note that the noble gases do not have an electronegativity. This is observed through Periodic Trends, as the further right of a period, and higher up a group are observed to have increased values in electronegativity. This scale ranges from 0.7 to 4.0, where cesium is the least electronegative element, and with fluorine being the most electronegative element. It was created by measuring the bond energy of the different elements joined by covalent bonding. The scale that was formed in order to measure this property is the Pauling scale. Which properties can be identified using periodic trends? Electronegativity:Įlectronegativity is a property that measures the tendency of an atom to attract electrons to form a bond. We discuss trends for properties such as electronegativity, atomic radius, first ionization energy, reactivity and electron affinity. This is due to the structural similarities’ elements have within a period or family that allows for these trends to take place.

These trends have allowed scientists in the past to predict certain characteristics of unknown elements. Periodic trends are observable patterns in the properties of an element that are dependent on its position in the Periodic Table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
